In spite of the current extraordinary situation with COVID-19, we are still offering our customers high-quality service of routine work and scientific projects. Right now, we are developing applications based on the usage of 2H peak integral as a universal internal standard in the common qNMR workflow. Recently, the German patent invented by our CEO Prof. Dr. Bernd Diehl was released, where the possibilities of using 2H signal for heteronuclear qNMR as well as for the determination of deuterium content in any given molecule were described (“Verfahren zur heteronuklearen quantitativen Bestimmung mittels NMR-Spektroskopie, Referenzsubstanzen hierfür und Verfahren zur Bestimmung des Deuterierungsgrades einer deuterierten Verbindung”). We would like to present you our new methodology to determine the degree of deuterated solvents – also as a service for YOU! Interested? Contact us!
qNMR Basics
As you know, in qNMR spectroscopy a quantity of analyte is determined based on comparison of its signal intensity with that of a reference substance in the same sample solution. In contrast to chromatographic methods, the reference substance in qNMR spectroscopy does not have to be identical to the analyte to be determined.
Standard Substances
In cases where several substances with different types of active nuclei have to be determined, a multi-nuclei standard can be used, which, in addition to carbon and hydrogen, also contains phosphorus, nitrogen and fluorine. However, for some active nuclei, especially inorganic anions and cations (sodium, potassium, chlorine, bromine and aluminum), no suitable standard substances are available. Another fundamental problem with external calibration is that no measuring cells with a defined volume are available in NMR spectroscopy. The volume of the commercially available NMR tubes is not standardized and, depending on the quality, its uncertainty can reach 10%.
Our New Method: All NMR-active nuclides can be simultaneously determined
We overcome the shortcomings of qNMR described above we invent a novel method, where all NMR-active nuclides can be quantified in a simple and precise manner. The idea is based on the knowledge that the deuterated solvent used for sample preparation can also serve as an internal standard, and thus all NMR-active nuclides in the sample solution can be simultaneously determined. The idea stands in contrast to the usual practice of qNMR spectroscopy, in which the same nuclide has to be present both in the standard and analyte.
Degree of Deuterated Solvents: Example CDCl3
Knowledge of the deuteration degree of common deuterated solvents is important for qNMR practice. Our novel methodology is naturally well suited for this! Let us show an example of deuterated CDCl3. According to the manufacturer’s information, the degree of deuteration of the CDCl3 used in the present example is approximately 99.8%. Thus, some of the solvent molecules represent CHCl3. So, we mixed deuterated solvent with isopropanol-d6, which contains defined number of D and H nuclei.
1H-NMR and 2H-NMR Spectra
In 1H-NMR spectrum you can see an intensive signal of CH-groups at δ 4.0 ppm and partially hydrogenated CD3 groups at δ 1.2 ppm of our reference compound. Moreover, you can observe non-deuterated CHCl3 molecules (Fig. 1). Only the dominant CD3 group and CDCl3 are visible in the 2H-NMR spectrum (see Fig. 2).
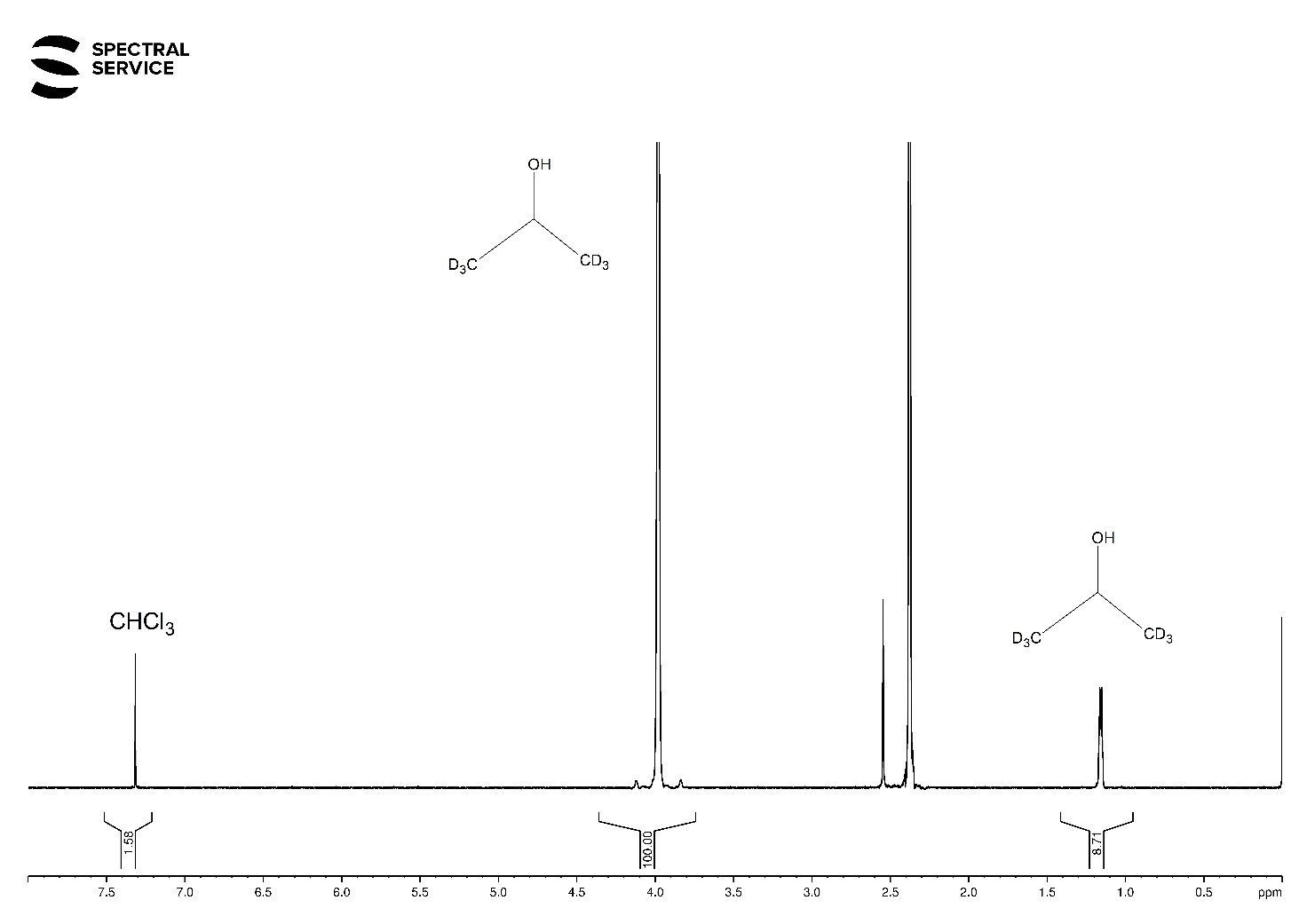
Fig. 1. 1H-NMR spectrum of deuterated chloroform mixed with isopropanol-d6.
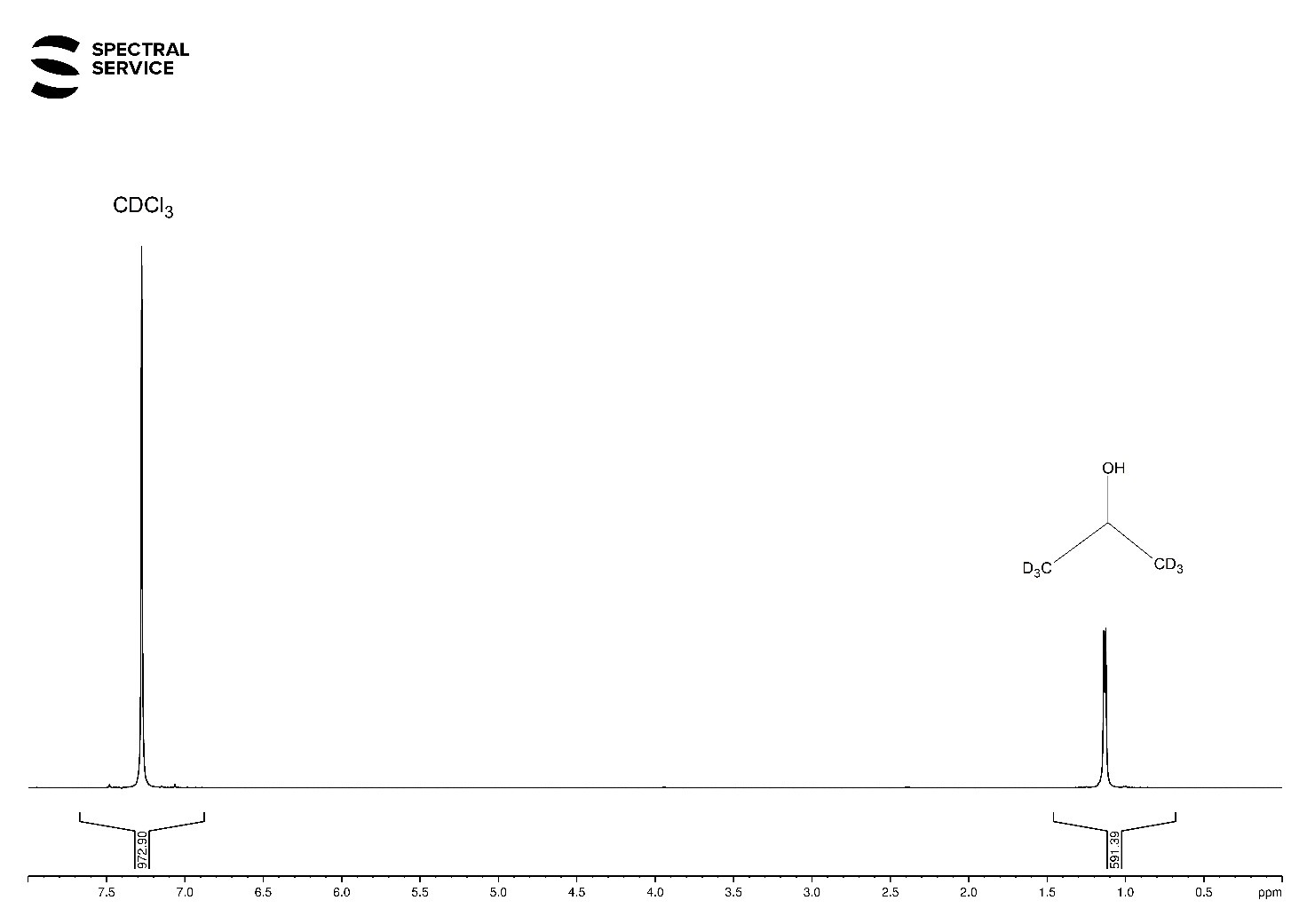
Fig. 2. 2H-NMR spectrum of deuterated chloroform mixed with isopropanol-d6.
Knowing integral areas of both D and H of isopropanol and deuterated solvent, it is possible to simply calculate the degree of deuteration. The advantage in comparison with classical approach is that we do not need to weight both compounds. We validated our method using classical qNMR approach with internal standard and standard addition method. Other characteristics (precision, reproducibility, robustness) were calculated. The developed method was applied on the determination of degree of deuterated solvents such as MeOD, ACN, CDCl3, acetone, benzene, DMSO-d6.
Routine NMR Applications
We are planning to increase the number of routine NMR applications based on the proposed method. Similar to deuterated solvents it is of course possible to check the quality of any given deuterated molecule. Another important area for such “standard-free analytics” is medicinal diagnostics and forensics. Using D2O as a reference we can, for example, significantly improve the determination of blood alcohol compared to conventional methods. The approach is acute and, probably, represents a future of qNMR in general.
Interested?
If you are intersted in our new methodology to determine the degree of deuterated solvents – you are highly welcome to contact us!